This guide covers common health problems and how they’re usually treated. We’ll talk about things like headaches, stomach pain, and other issues that many people face. Remember, it’s always best to talk to a doctor for personalized advice. They can figure out exactly what’s going on and how to help you feel better.
Headaches
There are various types of headaches, including tension headaches, migraines, and cluster headaches.Headaches are something most people experience at some point. They can feel like a constant ache or a sharp pain in different parts of the head. Often, they happen because of stress, not drinking enough water, or tension. If you have a mild headache, resting, drinking water, and relaxing can help. But if headaches happen a lot or are very strong, it’s important to talk to a doctor to figure out the best way to feel better.
Precautions
- Stay Hydrated: Dehydration can trigger headaches, so make sure to drink an adequate amount of water throughout the day.
- Maintain a Regular Sleep Schedule: Getting enough quality sleep is crucial in preventing headaches.
- Manage Stress: Practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga to reduce stress levels.
- Limit Screen Time: Prolonged exposure to screens can strain your eyes and lead to headaches. Take regular breaks, especially if you work on a computer.
- Watch Your Diet: Avoid skipping meals and try to maintain a balanced diet. Certain foods and drinks, like caffeine and alcohol, can trigger headaches in some people.
- Exercise Regularly: Physical activity helps reduce tension and stress, which can contribute to headaches.
- Maintain Good Posture: Poor posture, especially when sitting at a desk or using electronic devices, can lead to tension headaches.
Cures/Treatments:
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Common pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help alleviate headache pain.
- Cold Compress: Applying a cold compress or ice pack to the forehead or temples can provide relief.
- Rest in a Dark, Quiet Room: Find a calm space, close your eyes, and try to relax. This can be particularly effective for migraines.
- Caffeine: In some cases, a small amount of caffeine can help relieve headache pain.
- Aromatherapy: Certain scents like lavender or peppermint oil may provide relief for some individuals.
- Gentle Massage: Massaging the neck, shoulders, and temples can help relax tense muscles contributing to the headache.
Stomach Pain
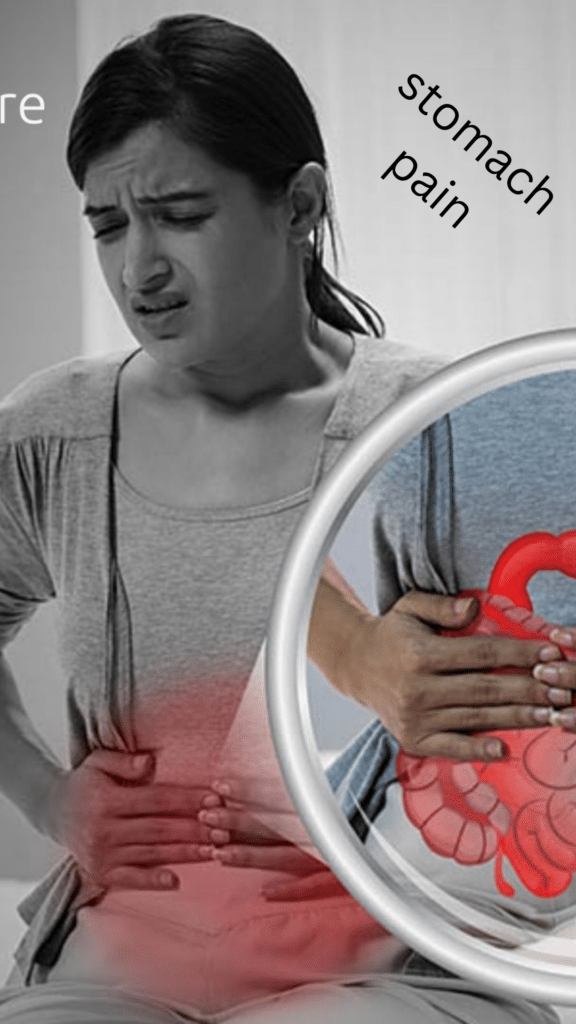

Stomach pain means feeling uncomfortable or hurting in the area between your chest and lower belly. It can range from a mild ache to a stronger pain. This can happen for different reasons like eating too much, having a tummy bug, or even just normal things like menstrual cramps. But sometimes, it can be more serious, like if you have an ulcer or a problem with your appendix. To feel better, you might need to take medicine, change what you eat, rest, or sometimes even have an operation. If your stomach hurts a lot or for a long time, it’s really important to talk to a doctor so they can figure out what’s going on and help you feel better.
Precautions:
- Balanced Diet: Eat a well-balanced diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Avoid overindulging in rich or spicy foods.
- Hydration: Drink an adequate amount of water daily to help maintain healthy digestion.
- Chew Food Well: Take your time when eating, and chew your food thoroughly to aid in digestion.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to promote healthy digestion and reduce the risk of constipation.
- Stress Management: Practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga to reduce stress, which can contribute to stomach discomfort.
- Avoid Trigger Foods: Identify and avoid foods that tend to cause you digestive problems or discomfort.
Cures/Treatments:
- Over-the-Counter Medications: Antacids or pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help alleviate mild stomach pain.
- Herbal Teas: Peppermint or ginger tea may provide relief from stomach discomfort.
- Heat Pad or Warm Compress: Applying heat to the abdominal area can help relax muscles and ease pain.
- Probiotics: These “good” bacteria can help restore the balance of microorganisms in your digestive system.
- Fiber Supplements: If constipation is a concern, fiber supplements can help regulate bowel movements.
- Rest and Relaxation: Taking a break and finding a comfortable position to lie down can provide relief.
Common Cold
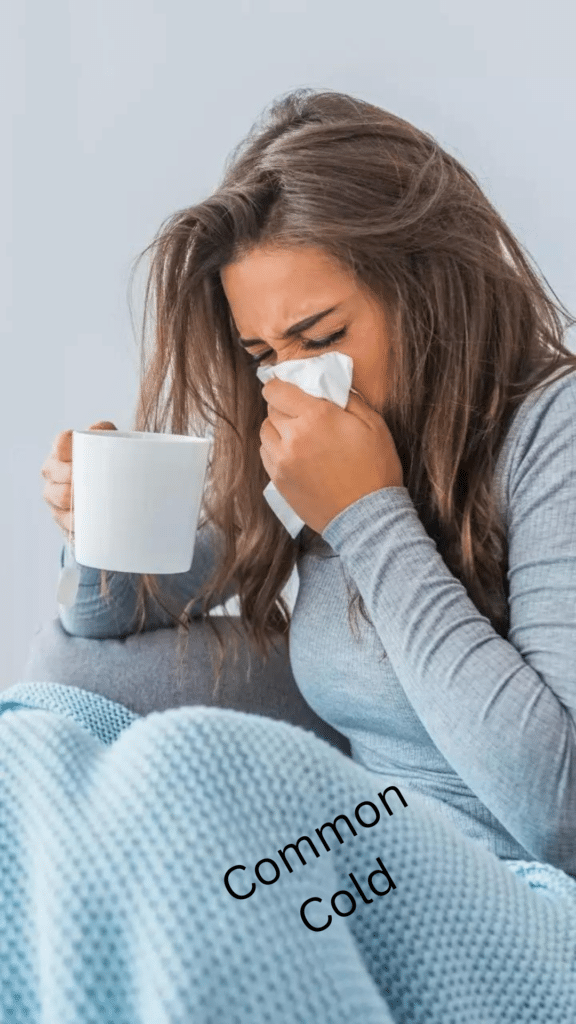

The common cold is a sickness caused by a virus. It gives you a runny or stuffy nose, sneezing, coughing, and sometimes a sore throat or mild fever. You can catch it from others who are sick. To avoid it, wash your hands often and stay away from sick people. Rest, drink fluids, and use medicine from the store can help you feel better. If you don’t get better or feel worse, talk to a doctor.
Precautions:
- Frequent Handwashing: Wash your hands regularly with soap and water, especially after being in public places or touching surfaces that others may have touched.
- Avoid Touching Face: Try not to touch your face, especially your eyes, nose, and mouth, as this can transfer viruses from your hands.
- Cover Your Mouth and Nose: Use a tissue or your elbow when coughing or sneezing to prevent the spread of germs.
- Avoid Close Contact: Try to stay away from people who are sick, and if you’re feeling unwell, consider keeping your distance from others to prevent transmission.
- Clean and Disinfect Surfaces: Regularly clean and disinfect frequently-touched surfaces like doorknobs, light switches, and countertops.
Cures/Treatments:
- Rest: Get plenty of rest to help your body recover and strengthen its immune response.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids like water, herbal teas, and clear broth to stay hydrated, which helps your body fight off the virus.
- Over-the-Counter Medications: Over-the-counter remedies like decongestants, pain relievers, and cough suppressants can help alleviate symptoms.
- Warm Liquids: Hot beverages like herbal tea, warm water with honey, or chicken soup can help soothe a sore throat and provide comfort.
- Gargle with Warm Salt Water: This can help ease a sore throat and reduce irritation.
- Use a Humidifier: Adding moisture to the air can help ease congestion and soothe irritated nasal passages.
Influenza (Flu):

The flu, short for influenza, is a sickness caused by tiny germs. It makes you feel hot, with a cough, body aches, and sometimes a sore tummy. You can get it from someone who’s sick when they cough or sneeze. To stop it from spreading, wash your hands a lot and consider getting a special shot called a vaccine. If you do get sick, rest, drink fluids, and maybe take medicine from the store. If you don’t feel better or if you’re very sick, talk to a doctor. They can help you get better.
Precautions:
- Get Vaccinated: Getting a flu vaccine is one of the best ways to prevent influenza. It helps your body build up defenses against the virus.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Wash your hands often with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, especially after being in public places or touching surfaces that others may have touched.
- Avoid Close Contact: Try to stay away from people who are sick. If you’re feeling unwell, consider keeping your distance from others to prevent spreading the virus.
- Cover Your Mouth and Nose: Use a tissue or your elbow when coughing or sneezing to prevent the spread of germs.
- Clean and Disinfect: Regularly clean and disinfect frequently-touched surfaces like doorknobs, light switches, and countertops.
Cures/Treatments:
- Rest: Get plenty of rest to help your body recover and strengthen its immune response.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids like water, herbal teas, and clear broth to stay hydrated, which helps your body fight off the virus.
- Over-the-Counter Medications: Over-the-counter remedies like antiviral medications, pain relievers, and cough suppressants can help alleviate symptoms.
- Warm Liquids: Hot beverages like herbal tea, warm water with honey, or chicken soup can help soothe a sore throat and provide comfort.
- Gargle with Warm Salt Water: This can help ease a sore throat and reduce irritation.
- Use a Humidifier: Adding moisture to the air can help ease congestion and soothe irritated nasal passages.
Allergies
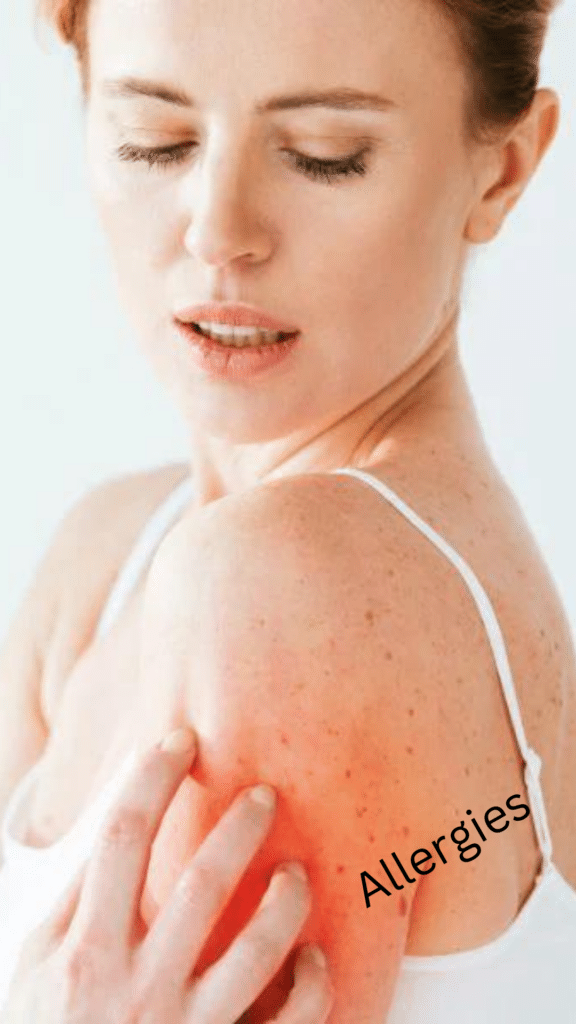

Allergies happen when the body reacts to certain things like pollen, pet fur, or certain foods. This can cause symptoms like sneezing, itchy eyes, or a rash. The best way to deal with allergies is to avoid the things that cause them. Sometimes, over-the-counter medicines can help, but if allergies are severe, a doctor might suggest allergy shots to help the body get used to the allergens. If you think you have allergies, talking to a doctor can help find the best way to manage them.
Precautions:
- Identify Triggers: Try to figure out what specific allergens are causing your reactions. This can help you take steps to avoid them.
- Keep Indoor Air Clean: Use high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters in your home to trap allergens like pollen, dust mites, and pet dander.
- Limit Outdoor Exposure: On high pollen days, try to stay indoors, especially in the morning when pollen levels are usually higher.
- Close Windows and Use Air Conditioning: This can help keep pollen and other outdoor allergens from getting inside your home.
- Regular Cleaning: Vacuum and dust your home frequently to reduce allergens like dust mites and pet dander.
Cures/Treatments:
- Over-the-Counter Antihistamines: These can help relieve symptoms like sneezing, runny nose, and itching.
- Decongestants: These can help with nasal congestion, but they should be used with caution and under a doctor’s guidance.
- Nasal Corticosteroids: These sprays can help reduce inflammation and congestion in the nasal passages.
- Allergy Shots (Immunotherapy): For severe allergies, allergists can provide a series of shots that gradually expose your body to allergens, helping it build up a tolerance over time.
- Avoidance of Allergens: This is the most effective way to prevent allergic reactions. For example, if you’re allergic to pollen, staying indoors on high pollen days can help.
Back Pain
Back pain is a common discomfort felt in the area between the lower ribs and the buttocks. It can range from a dull ache to a sharp, intense pain. Common causes include muscle strains, herniated discs, and underlying medical conditions. To prevent back pain, maintaining good posture, regular exercise, and proper lifting techniques are essential. If back pain persists or worsens, seeking medical advice is important for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment options.
Precautions:
- Maintain Good Posture: Whether sitting, standing, or lifting, keeping your spine aligned can help prevent unnecessary strain on your back.
- Exercise Regularly: Engage in activities that strengthen your back and core muscles, which can provide support and stability.
- Lift Properly: When lifting heavy objects, use your legs rather than your back to avoid straining the muscles.
- Use Ergonomic Furniture: Ensure that your workspace and furniture are set up in a way that supports good posture and reduces strain on your back.
- Avoid Prolonged Sitting or Standing: Take breaks to move around and change positions if you’re in one posture for an extended period.
Cures/Treatments:
- Rest: Take a break and avoid activities that may exacerbate the pain. Gentle stretching or light activities like walking can help.
- Heat or Cold Therapy: Applying a hot or cold compress to the affected area can provide relief from muscle soreness and inflammation.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Non-prescription pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help alleviate mild to moderate pain.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can provide exercises and techniques to strengthen your back and improve flexibility.
- Massage or Chiropractic Care: These therapies can help relax tense muscles and improve spinal alignment, providing relief from back pain.
- Prescription Medications: For severe or chronic pain, a doctor may prescribe stronger medications or muscle relaxants.
- Injections or Procedures: In some cases, injections of medications or certain procedures may be recommended to alleviate pain.
Diarrhea

Diarrhea is when you have very runny poop often. It happens because of germs, bad food, or some medicines. This can make you lose a lot of water from your body. To feel better, drink lots of water and eat simple foods like crackers or rice. If it doesn’t stop, talk to a doctor for help.
Precautions:
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids like water, clear broth, or oral rehydration solutions to replace the lost water and electrolytes.
- Avoid Dairy and High-Fiber Foods: These can make diarrhea worse, so it’s best to stick to bland, easily digestible foods like rice, bananas, and toast.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Wash your hands thoroughly after using the bathroom and before preparing or eating food to prevent the spread of germs.
- Avoid Trigger Foods: If certain foods or drinks seem to worsen your diarrhea, try to avoid them until you’re feeling better.
Cures/Treatments:
- BRAT Diet: This stands for Bananas, Rice, Applesauce, and Toast – these are gentle foods that can help firm up stool.
- Over-the-Counter Medications: Anti-diarrheal medications like loperamide can provide relief by slowing down bowel movements.
- Probiotics: These “good” bacteria can help restore the balance of microorganisms in your digestive system.
- Avoid Caffeine and Alcohol: These can irritate your digestive system and make diarrhea worse.
- Rest: Get plenty of rest to help your body recover.
Insomnia

Insomnia is when it’s tough to fall asleep, stay asleep, or get good sleep. It can make you feel tired and grumpy during the day. Stress, anxiety, or some medicines can cause it. To sleep better, have a bedtime routine, make your bedroom cozy, and avoid things like caffeine or screens before bed. If you still can’t sleep, talk to a doctor for advice.
Precautions:
- Establish a Sleep Routine: Try to go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends. This helps regulate your body’s internal clock.
- Create a Relaxing Bedtime Routine: Engage in calming activities before bed, like reading a book, taking a warm bath, or practicing deep breathing exercises.
- Optimize Your Sleeping Environment: Ensure your bedroom is comfortable, quiet, and cool. Use comfortable bedding and consider using blackout curtains to block out light.
- Limit Screen Time: Avoid screens like phones, tablets, and computers at least an hour before bedtime, as the blue light emitted can interfere with your ability to fall asleep.
- Avoid Stimulants: Stay away from caffeine, nicotine, and other stimulants in the hours leading up to bedtime.
Cures/Treatments:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I): This structured program helps address thoughts and behaviors that may be contributing to your insomnia.
- Relaxation Techniques: Practices like progressive muscle relaxation, deep breathing exercises, and meditation can help calm your mind and prepare your body for sleep.
- Limit Daytime Naps: If you nap during the day, try to keep it short (20-30 minutes) and avoid napping too close to bedtime.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can help regulate your sleep-wake cycle, but avoid intense exercise close to bedtime.
- Limit Alcohol and Caffeine: These substances can disrupt your sleep, so it’s best to avoid them, especially in the hours leading up to bedtime.
- Avoid Heavy Meals Before Bed: Eating a large, heavy meal late in the evening can disrupt your ability to fall asleep comfortably.
In conclusion, knowing how to effectively deal with everyday health problems gives us the power to take charge of our well-being. Whether it’s headaches, stomachaches, allergies, or sleep troubles, understanding what to do can make a big difference. Remember, while these tips are helpful, talking to a doctor is really important for the best advice. So, with a mix of self-care and expert help, we can face health issues with confidence!
